Your Dental Guide to Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Learn more about Gingivitis and Periodontitis, the Symptoms of Gum Disease, and Cure
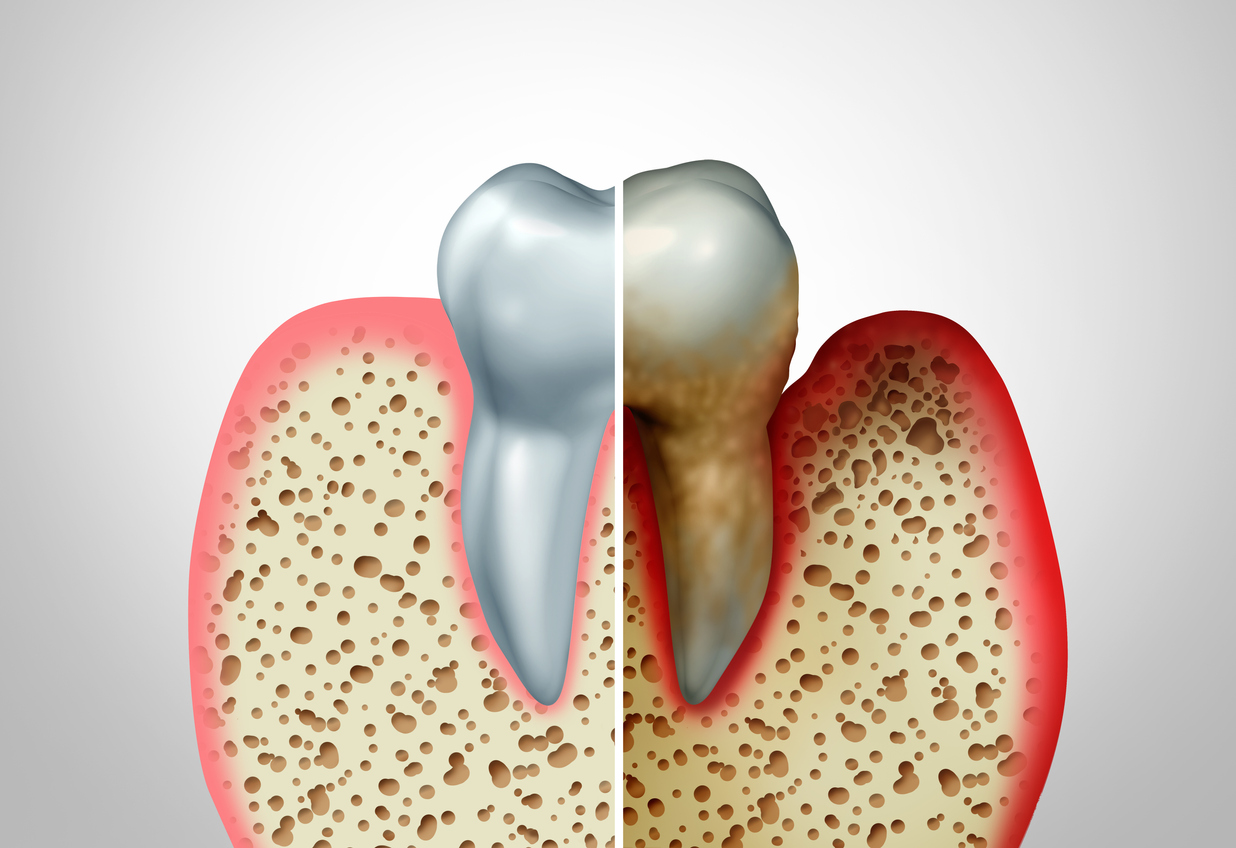
What is Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common ailment of the gums that causes inflammation as a result of bacterial growth. If you find blood on your toothbrush or when flossing, that may be considered one of the first signs of such gum disease. It should be treated as soon as possible or it can lead to periodontal disease.
Key Differences Between Gingivitis and Periodontitis, the Stages of Gum Disease
Gingivitis and periodontitis are both gum problems but the former entails gun inflammation, while the latter entails gum disease. Moreover, gingivitis usually precedes the periodontitis, but it is important to note that not all forms of gingivitis build up to periodontitis.
In the early stages, gingivitis symptoms involve a build up of bacteria, which in turn causes the gums to become inflamed. As a result, they bleed easily while brushing or flossing. However, it is important to note that the teeth themselves are still held firmly in place and there is no damage to the tissues, or the bone structure.
If this is left untreated, these early gingivitis symptoms can sometimes lead to periodontitis. This particular form of gum disease causes the inner layer of the gum as well as the bone to be separated from the teeth and subsequently form pockets. As a result, these pockets can easily become filled with food debris and thus become infected.
While the body’s immune system battles these infections, the aforementioned bacterial plaque spreads below the gum line. The emission of toxins by both sides (the bacteria as well as the enzymes involved in fighting the infection) result in the breakdown of the bone and connective tissues that hold the teeth in their place.
With the progression of this gum disease, the pockets enlarge, and further breakdown of bone and connective tissue occurs. This makes the teeth loose and can lead to tooth loss. This form of gum disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults.
What are Some Causes of Gum Disease
Plaques resulting from bacterial growth are usually the primary cause of gum disease. However, the following factors can also be causative agents when it comes to periodontal disease:
- Changes in hormone levels e.g. during pregnancy or puberty etc., sometimes end up making the gums more sensitive and thus more susceptible to gingivitis.
- Diseases that compromise the immune system e.g. cancer, or diseases like diabetes which compromise the body’s blood sugar levels, can all result in the patient being more susceptible to infections from bacteria and therefore more open to gum disease such as gingivitis and periodontal disease; not to forget cavities in such cases.
- Sometimes, medications can also lead to gum disease. Some that lessen the production of saliva which is a protective agent of gums and teeth, can contribute to a gum disease like gingivitis.
- It’s no surprise that smoking also results in gum disease since it makes it difficult for gum tissue to repair itself in line with the body’s natural order of things.
- Not brushing or flossing regularly can also lead to gum disease such as gingivitis since poor hygiene is a prerequisite for the development of bacterial plaque.
- Gum disease can also be hereditary. Family history of gum disease will make a person more vulnerable to diseases such as gingivitis.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease
Gum disease symptoms are usually painless and subtle and, therefore, progress without the patient being aware at times. However, there may be some warning signs. There are symptoms that illustrate how it may be one form of the disease or the other, depending on the severity. Some commonplace symptoms of gum disease follow:
- Bleeding gums both during and post brushing.
- Swollen gums that may appear reddish and/or feel tender.
- Constant bad breath or a corresponding taste in the mouth.
- Gums starting to recede.
- Pockets forming between the teeth and the gums.
- Teeth feeling lose or changing positions.
- Feeling that the teeth do not fit together like they used to upon biting down.
Even if the above symptoms are not noted it does not mean that a person does not have some form of a gum disease. Some forms only affect certain teeth like the molars in the back and so might make it harder for symptoms to appear obviously visible. A periodontist or a dentist are the only people qualified to determine if a person has a gum disease or not.
How Can Your Dentist Treat Gingivitis?
Gingivitis treatment can be approached from different ways. The following are some of the options on that score:
- Scaling and Root Planning (SRP) is a non-invasive but vigorous method of deep cleaning that is sometimes handy in this particular gum disease treatment method. The scaling involves the scraping away of bacterial plaque on either side of the gum line, while root planning involves the evening out of the tooth root to prevent bacteria from making a foothold. This is usually made easier by uneven spots on the tooth root such as nooks and crannies. This also aids the gums in getting reattached to the teeth.
- Another form of gum disease treatment or, more specifically, gingivitis treatment is curettage. It involves the use of a wee handheld tool known as a curette which is used to scrape away infected/damaged gum tissue and helps the remaining structure to heal. Antibiotics are usually prescribed following this method of gum disease treatment.
- When non-invasive techniques do not work when it comes to gingivitis treatment, flap surgery is employed by your dentist. Usually comes into use in the advanced stages of periodontal disease. As the name indicates incisions around the infected area are made which allows the gum tissue to be lifted and held like a flap while the area underneath including the tooth root is cleaned. The tissue is then sowed back into place decreasing pocket sizes.
- If damage has occurred to the bone as a result of gingivitis or any other gum disease, bone grafts can be performed in which the eroded or damaged parts of the bones are replaced with grafts allowing the bone to regrow and for the teeth to stabilise.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Gingivitis Treatment Really Work?
Gingivitis treatment, depending on the phase of the gum disease, can actually work in the sense that it can reverse the damage. For example, if caught earl,y gingivitis can be undone by following three simple steps: visiting the dentist regularly for clinical cleanings, brushing your teeth regularly (preferably twice a day), and flossing regularly as well.
Anti-bacterial mouthwash can be used regularly as well to keep the mouth bacteria free which in turn will prevent any plaque development which is the first step towards any gum disease including, but not limited to, gingivitis. However, if not caught early, gingivitis causes (as we read above) periodontal disease which in its advanced stages can cause irreversible damage.
How Lengthy Can the Treatment for Gingivitis Be?
The length of the treatment depends on various factors. Gingivitis causes periodontitis if not treated and depending on the magnitude of the infection it may take quite some time with the patient visiting his/her dentist regularly for cleaning.
It also depends on the treatment being employed and how good the patient is with oral health routine at home: do they brush and floss regularly or not, for example. Early stages of gingivitis can be removed in approximately two weeks with good care.
What are Some Advantages of Gum Treatment
Gingivitis treatment can benefit you in a variety of ways, some of which are as follows:
- Removes painful factors like swollen gums.
- Prevents loose or shifting teeth and, therefore, tooth loss.
- Helps get rid of bad breath.
- Aids in maintaining healthy teeth and gums.
- Prevents the genesis and/or spread of bacteria.
- Minimises the risk of bone damage and/or loss.
- Beneficial for your smile’s appearance.
- Helps with your health, holistically.
- Beneficial for your quality of life.
How Does Scaling and Root Planning Help?
As we know, gingivitis causes damage to your oral health and one of the treatments for this gum disease is SRP (Scaling and Root Planning). It is a non-invasive method of vigorous cleaning i.e. scraping away plaque from the teeth and gums and smoothing out teeth roots to prevent them from being loose or shifting.
Your dentist will determine, after a careful examination of your gums and teeth, whether you are a suitable candidate for the treatment or not. There are of course risks with every treatment in the form of side effects, depending on the patient and their particular condition. But generally, SRP is not damaging to the oral health of the patient. Scaling does not damage teeth and smoothing out of a tooth root is also not detrimental.
What are Easy Ways to Prevent Gum Disease
Gum disease causes significant damage and if the following steps are taken seriously, the chances of preventing it are very high.
- Brushing twice a day every day and flossing daily or as per your dentist’s instruction, who is familiar with your case.
- Using fluoride toothpaste specifically and regular rinsing with the same toothpaste is also recommended.
- Use smoother and softer toothbrush that have less of a chance of puncturing or damaging your gums with rigorous brushing.
- Replacing your toothbrush every three months or so.
- A healthy diet and avoiding food items with a high sugar content whenever possible.
- Tobacco products like snuff and cigarettes should be avoided as they cause significant damage to oral health, and even overall health.
- Regular visits to the dentist who will be able to detect otherwise hidden plaques and remove them and/or plaques that have so far not been removed by regular brushing and flossing.
By following these methods you will develop a habit of good oral hygiene and, therefore, help prevent any sort of gum problems.